Building physics - the most important component for a good life cycle assessment in construction
Climate-friendly building and renovation - building physics is the key
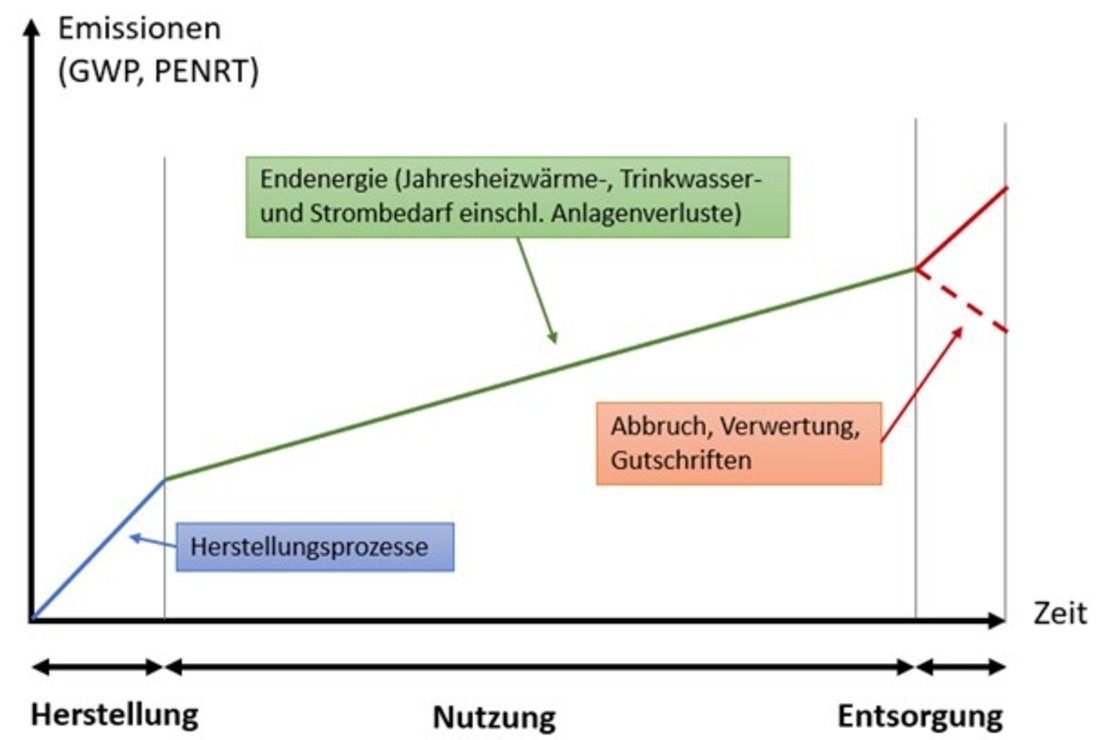
Life cycle assessment (LCA) in construction deals with the ecological effects of building measures. It essentially looks at the production, use and disposal phases. In each of these life cycle phases, material and energy flows arise from the extraction of raw materials, their processing, transport, use and disposal - the so-called grey energy. The material and energy flows are linked to impact indicators such as the "global warming potential" GWP [kg CO2-eq.] or the "non-renewable primary energy" PENRT [MJ]. The GWP, which in everyday language is simplified as CO2 consumption, is one of the most important factors in determining the LCA.
CO2 -savings in construction - what is effective?
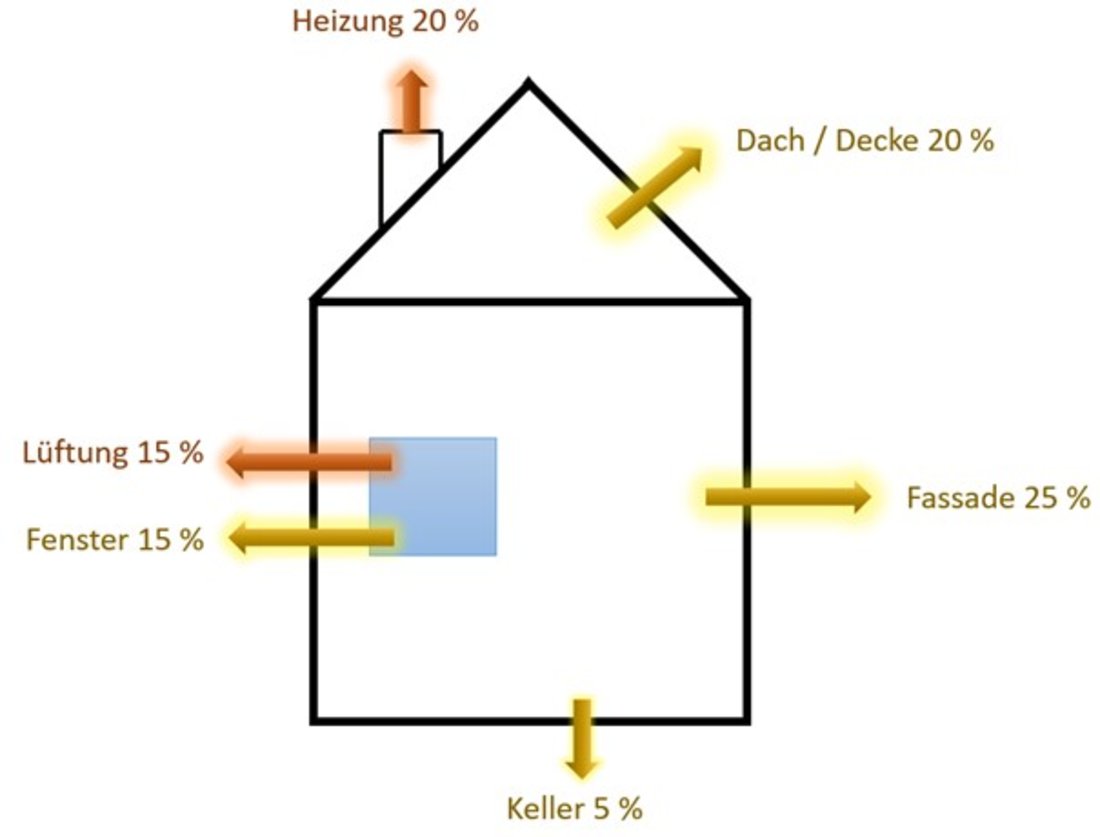
A building is usually used for over 100 years and many emissions can occur over this period. In existing buildings, the energy demand during the use phase has the greatest impact on the life cycle assessment if fossil fuels are used and insulation is inadequate or non-existent. High heat energy losses occur due to leaks in the thermal building envelope. These transmission heat losses consist of energy losses through the building components as well as energy losses through thermal bridges.
We at goodmen energy carry out building physics measurements and measures for this purpose. As a rule, the greatest energy and CO2 savings can be achieved by insulating facades, ceilings and roofs.
- From a building physics point of view, the most CO2 can be saved through a tight building envelope.
In addition, efficient systems engineering with renewable energy sources plays a major role in successfully saving CO2, energy and ultimately operating costs in the building. More information on this can be found in our blog post "Rising energy costs? Focus on efficiency now".
Eco-balance of the building materials
The building materials that are used are crucial to reducing the emissions that occur during the manufacturing and disposal phases.
Certificates already exist for many building materials, such as the Blue Angel eco-label and the Concrete Sustainability Council (CSC) certificate for concrete, demonstrating their environmental friendliness.
When it comes to insulation materials, there is a discrepancy between highly efficient and ecological materials. The mineral, biological and renewable insulating materials usually have worse insulating properties than synthetic materials. On the other hand, they have the advantage of being naturally better at regulating moisture.
Depending on the project, we weigh up and work out the best solution - whether it is highly energy-efficient, particularly ecological or a mixture of both.
The German Government - New Concepts for Sustainable Building
The German government has been providing incentives for energy-efficient construction for some time now. Through promotional loans and grants from the KfW Bank, building owners can receive up to 25% of their construction costs for new buildings and up to 50% for renovations. We of goodmen energy provide you for this the request and set it to us to act both pollution free and economically.
The new traffic light government would like to go still another step further and addresses in the new coalition agreement now also the ecological balance of the building materials. It wants to take a closer look at the use of gray energy and lifecycle costs. Among other things, a digital building resource passport is to be introduced. We have already dealt with this issue in detail and are working with project partners on database-based software to better filter out ecological building materials from the large number of products.